negative permeability materials|left handed materials : solution Here we introduce materials with negative static permeability as a new paradigm for manipulating magnetic fields. As a first step, we extend the solutions of Maxwell magnetostatic . Bước 2: Tham gia danh sách chờ. Bạn cần phải truy cập trang “Tổng quan về Bing Mới” và nhấp vào nút “Tham gia danh sách chờ”. Sau đó, Microsoft sẽ gửi cho bạn một email để xác nhận đơn đăng ký của bạn.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webIf you have Telegram, you can view and join Scarlet IOS | iPhone IPA right away.
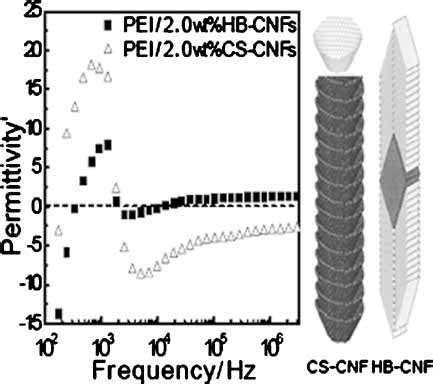
We confirm the theory by experimentally creating a spherical shell that emulates a negative-permeability material in a uniform magnetic field. Our results open new possibilities . Left-handed materials require negative permeability µ, an extreme condition that has so far been achieved only for frequencies in the microwave to terahertz range7,8,9,10,11.
Here we introduce materials with negative static permeability as a new paradigm for manipulating magnetic fields. As a first step, we extend the solutions of Maxwell magnetostatic . We propose a novel way to achieve an exceptionally wide frequency range where metamaterial possesses negative effective permeability. This can be achieved by employing . Nearly all familiar materials, such as glass or water, have positive values for both ϵ and μ. It is less well recognized that materials are common for which ϵ is negative. Many metals—silver and gold, for example—have .The split ring resonator (SRR) medium recently introduced by Pendry et al. [6] has now given us the opportunity to make a material with nega-tive permeability, from which a left-handed .
single negative metamaterials
nylon magnetic permeability
‘Negative-index materials’, as first proposed, required the permittivity, ɛ, and permeability, μ, to be simultaneously less than zero, but such materials face limitations. Here, .
Here, a metamaterial configuration is conceived that judiciously generalizes the traditional electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) scheme—by which radiation losses .Here we first present a brief background and the history of complex media, in particular the materials with negative permitivity and permeability, and then we discuss some of the .
negative refractive index metamaterials
Composite Medium with Simultaneously Negative Permeability and Permittivity D.R. Smith,* Willie J. Padilla, D.C. Vier, S.C. Nemat-Nasser, and S. Schultz . dinary materials. An example medium is a three-dimen-sional array of intersecting thin straight wires, for which As the ferrites used in these metamaterials are soft magnetic materials, in order to realize the FMR and negative permeability, an external magnetic field must be applied around the ferrites .Here the author presents a brief background and the history of complex media, in particular the materials with negative permittivity and permeability, and then he discusses some of the salient electromagnetic features of these metamaterials. This is followed by description of some of the ideas regarding potential future applications of these metamaterials in devices and .The SI unit for permeability is the square metre (m 2).A practical unit for permeability is the darcy (d), or more commonly the millidarcy (md) (1 d ≈ 10 −12 m 2). The name honors the French Engineer Henry Darcy who first described the flow of water through sand filters for potable water supply. Permeability values for most materials commonly range typically from a fraction to .
negative refractive index materials
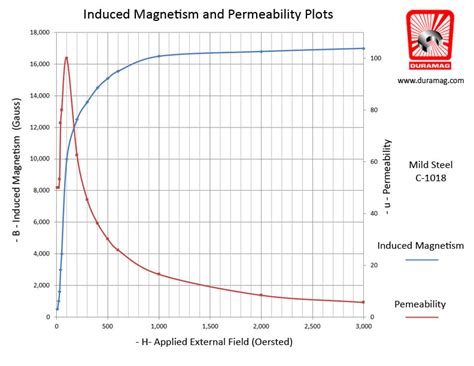
A negative permeability has been obtained above 5 GHz due to the natural magnetic resonance in the 70 vol % particle content composite material. In this content, electrical permittivity spectra show a nonmetallic characteristic. This permeability dispersion can be applied for the left-handed media. Left-handed materials require negative permeability µ, an extreme condition that has so far been achieved only for frequencies in the microwave to terahertz range7,8,9,10,11. Extension of the . Also be aware that materials exhibiting high permeability are also typically non-linear; that is, permeability depends on the magnitude of the magnetic field. Again, values reported here are those applicable to applications in which these materials are typically used. Free Space (vacuum): \(\mu_r\triangleq 1\).The understanding of these new solutions allow us to devise a negative-permeability material as a suitably tailored set of currents arranged in space, overcoming the fact that passive materials with negative permeability do no exist in magnetostatics. We confirm the theory by experimentally creating a spherical shell that emulates
HFSS was the first general-purpose software product to solve arbitrary three-dimensional electromagnetic field problems. 16,17 This paper first described the basic principle and design process of Left-handed material and Split-ring resonators. Then, by using the HFSS10.0 software of Ansoft company, we analyzed and simulated the three-dimension . Materials with either negative permittivity or negative permeability support a host of surface modes closely related to surface plasmons, commonly observed at metal surfaces , and it is these states that are resonantly excited. By amplifying the decaying fields of a source, the surface modes restore them to the correct amplitude in the image plane. For materials at optical frequencies, the dielectric permittivity ε is different from that in vacuum. In contrast, the magnetic permeability μ for naturally occurring materials is close to its .
TL;DR: depending on the frequency, the free electrons react with a large lag with respect to the driving field, thus making the real part of $\epsilon$ negative (damped oscillator model). The permittivity links the displacement field $\textbf{D}$ to the electric field $\textbf{E}$. Roughly speaking it just tells you how much the material reacts to an electric field. Magnetic permeability refers to a material’s ability to allow the passage of magnetic field lines. It is a fundamental property that helps determine the magnetic behavior of different materials and quantifies how easily they can be magnetized in the presence of an external magnetic field. Materials with high permeability are considered highly .
negative refraction material
We have studied the complex permeability spectra of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) under external magnetic field and permalloy composite materials, in which the heat treated peramalloy particles were embedded, in the microwave region to realize the negative permeability which is produced by the magnetic resonance. In this report, we discuss the characteristics of the negative .
universal hardness tester
Therefore, it degrades the device performance. As a technique for suppressing skin effect loss, a multilayer transmission line using a negative permeability material, which has negative permeability because the .The negative sign is due to the fact that the fluid flows down (negative) the hydraulic gradient from higher values to lower values. . Another term that arises when discussing flow through rocks and unconsolidated materials is .
permeability to be about −1 for the sample with thinner strips and −1.7 for the sample with thicker strips at wavelengths of 770 nm and 725 nm, respectively. OCIS codes: (160.4670) Optical materials, metamaterials, negative refraction, left-handed materials; (260.5740) Physical Optics, resonan ce; (310.6860) Thin films, optical properties.
portable hardness tester price
When such inclusions are embedded in a host medium, they may provide metamaterials with negative effective permeability at optical frequencies. We also show how the same inclusions may provide resonant electric dipole response and, when combining the two effects at the same frequencies, left-handed materials with both negative effective .Negative refraction can be obtained by using a metamaterial which has been designed to achieve a negative value for electric permittivity (ε) and magnetic permeability (μ); in such cases the material can be assigned a negative refractive index. Such materials are sometimes called "double negative" materials. [1] Negative refraction occurs at .Where, ϵ 0 is the electric constant; ϵ r is the relative permittivity; ϵ is the absolute permittivity of that material; Using Coulomb’s law, The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two point charges q 1 and q 2 separated by a distance r in free space can be calculated using relative permittivity(ϵ r).By taking “the ratio of electrostatic force(F a) between two point charges .
We demonstrate a composite medium, based on a periodic array of interspaced conducting nonmagnetic split ring resonators and continuous wires, that exhibits a frequency region in the microwave regime with simultaneously negative values of effective permeability μ eff (ω) and permittivity ɛ eff (ω).This structure forms a “left-handed” medium, for which it has .
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the resistance of a substance against the formation of a magnetic field. This constant is very important, since one of important magnetic properties is the relative permeability (dimensionless), the ratio of the permeability in a material to the permeability in a vacuum.The mathematical solution for Čerenkov radiation in a novel medium, left-handed medium (LH medium), which has both negative permittivity and permeability, is introduced in this paper. It is shown that the particle motion in the LH medium generates power that propagates backward. In this paper, both dispersion and dissipation are considered for the LH medium. The results . We have studied the complex permeability spectra of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) under external magnetic field and permalloy composite materials, in which the heat treated peramalloy particles were embedded, in the microwave region to realize the negative permeability which is produced by the magnetic resonance. In this report, we discuss the . The quest for negative refraction has brought the initial inspiration to the entire area of metamaterials research 1,2, and served as one of the main driving factors in this field over the last decade 3,4.Achieving a negative index in homogenisable materials normally involves making their effective permittivity and permeability simultaneously negative.
The relevance of negative permittivity and permeability was first theoretically disclosed by Veselago in 1968, . According to Wikipedia, natural materials with negative . 2 (b) shows that all the unit with different strip width process a negative effective permeability and the frequency of negative permeability decreases as the width increases, when the width increase from 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm, the frequency decrease form 6.78 MHz to 5.62 MHz. Thus, the frequency of negative permeability can be adjusted by the width .
micro vickers hardness tester
hard disk tester
webPrognósticos de Futebol. Prognósticos para hoje. Vitória da casa Mixco x Guastatoya. Por jogar 2.15. Mais de 2.5 Golos Guanacasteca x Cartaginés. Por jogar 1.83. Vitória da casa .
negative permeability materials|left handed materials